What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) and Why It Matters in New Zealand Industry
Non-Destructive Testing, or NDT, refers to a collection of analysis techniques used to evaluate the physical properties or structural integrity of materials and components without causing damage. Unlike destructive testing, NDT allows continued use of the part after inspection — a critical advantage when working with valuable or safety-critical components.
In New Zealand’s diverse industrial landscape, NDT serves as an invisible line of defence. Whether ensuring weld quality in fabrication, checking for corrosion in coastal installations, or validating repairs in ageing infrastructure, NDT provides the data to make confident, informed decisions — without delays or disassembly.
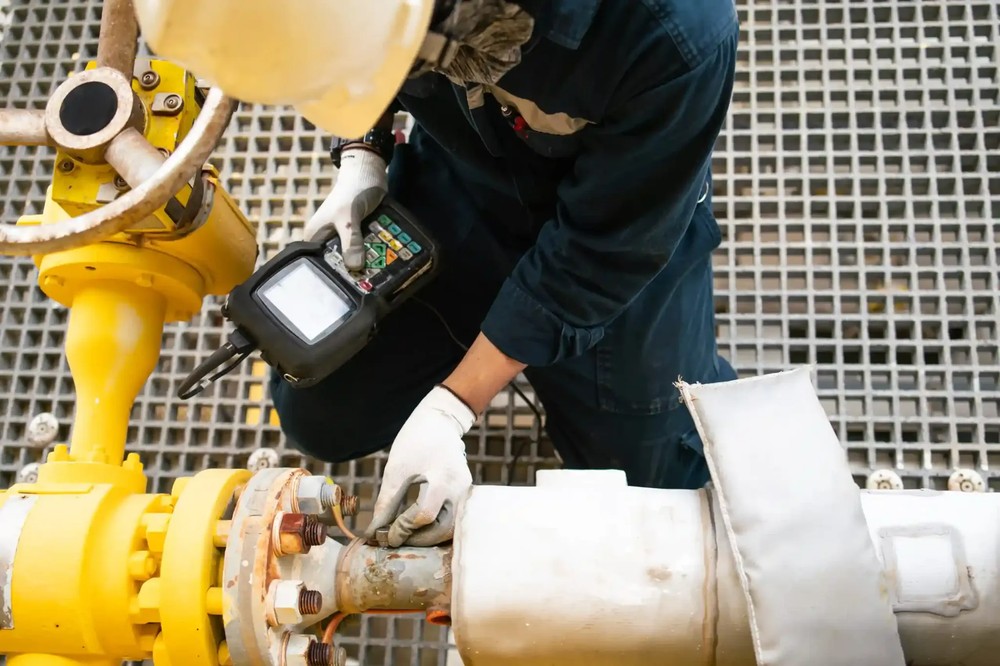

Why NDT Matters in New Zealand
Our environmental and regulatory landscape brings a unique set of challenges:
- Coastal Environment: Corrosive salt spray is a constant threat, especially to bridges, pipelines, and marine structures. Early-stage pitting, crevice corrosion, or under-deposit attack may remain invisible without targeted NDT.
- Seismic Sensitivity: Earthquake-prone zones demand high integrity in structural welds and anchor points. NDT helps verify weld fusion, detect fatigue cracks, and ensure reliable structural performance.
- Asset Ageing: Many industrial assets and public infrastructures were installed decades ago. Non-invasive inspection methods are essential to evaluate their integrity without interrupting service.
- Compliance Pressure: New Zealand’s engineering and manufacturing sectors face increasing demand for compliance with AS/NZS, ISO, and client-specific quality standards — many of which require validated NDT results.
In short: NDT is not optional — it’s a practical necessity.
Benefits of NDT You Can Trust
- Early Damage Detection: Find flaws that visual checks miss — including sub-surface cracks, porosity, weld root flaws, or internal voids.
- Cost-Effective Maintenance: Schedule preventive repairs before failures escalate. Avoid costly shutdowns or liability from undetected damage.
- Component Longevity: Monitor stress, corrosion, and fatigue to understand when replacement is truly necessary.
- Process Validation: Prove that your welding, casting, or forming process meets internal or client quality criteria.
- Traceable Results: Get formal reports and records suitable for quality audits, certifications, or third-party review.
Every test offers more than a “pass/fail” — it reveals the unseen, helping engineers, contractors, and asset owners make smarter choices.
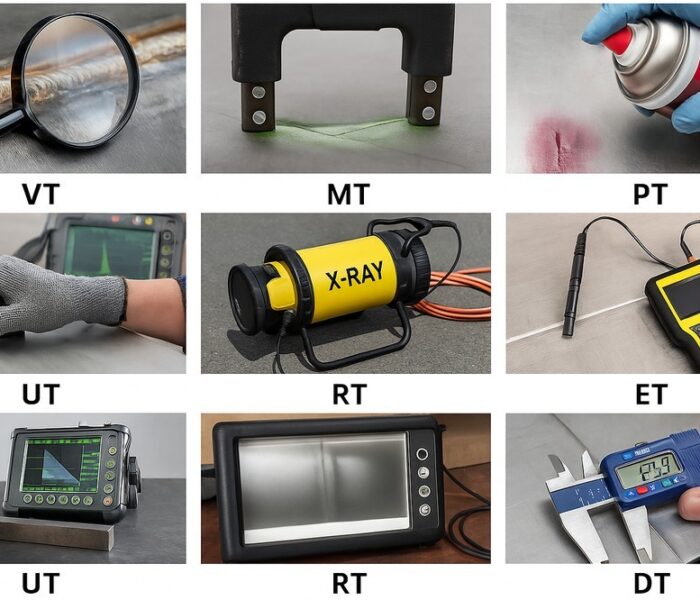
What Types of NDT Do We Perform?
At our lab, we offer several proven inspection techniques, each with specific strengths:
- Visual Testing (VT): The first step in any inspection — enhanced with good lighting, magnification, and standards for crack width, distortion, or surface anomalies.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): For ferromagnetic materials like carbon steel. A magnetic field is applied to the surface, and fine iron particles are sprayed across it. Surface and near-surface cracks become clearly visible where particles accumulate.
- Dye Penetrant Testing (PT): Used on non-magnetic metals like stainless steel or aluminium. A liquid dye is drawn into surface cracks by capillary action, then revealed by a developer. Great for finding hairline cracks, porosity, and laps.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): High-frequency sound waves are sent through the material. Discontinuities (like internal cracks or voids) reflect part of the wave back, which is measured on a screen. Suitable for thick welds, pressure vessels, and forged components.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): If applicable, RT uses X-ray or gamma radiation to generate internal images — particularly useful in complex welds and casting validation. It reveals voids, inclusions, lack of fusion, or root defects.
Each method is chosen based on material type, geometry, and the nature of expected defects.

The Bigger Picture — And What Comes Next
This overview only scratches the surface of what NDT can do. In future blog posts, we’ll break down each method in more detail — including real-world examples, sample reports, and what you can expect from the process.
Whether you’re validating a weld, checking for corrosion damage, or planning a preventive maintenance program, we can help you select the right test for the right material at the right time.
Have questions? Need a second opinion? Curious about which NDT method applies to your part or asset?
[Contact our lab here] — we’re happy to walk you through the options.


